Introduction to NSAVDEX
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) are a type of cryptocurrency exchange which allows for direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency transactions to take place online securely and without the need for an intermediary. Our mission is to pave the growth of DEFI adoption - this happens when the users feel confident to explore the blockchain space & developments are supported to build the future of decentralization. Decentralized financial services and making them openly accessible to anyone, anywhere in the world, NSAV launched its next Generation NSAVDEX.org, A production-ready cross-chain liquidity hub for all DeFi apps and financial services on OKEX chain.
Deal Terms
-
Reg-S
Offering TypeThe type of investments that can be made into this asset. -
$100
Min. InvestmentThe smallest investment amount that this asset is accepting.
Highlight

Unique Technical Architecture
Multi cross blockchain with ERC 20 protocols, OEC, formerly known as OKExChain,
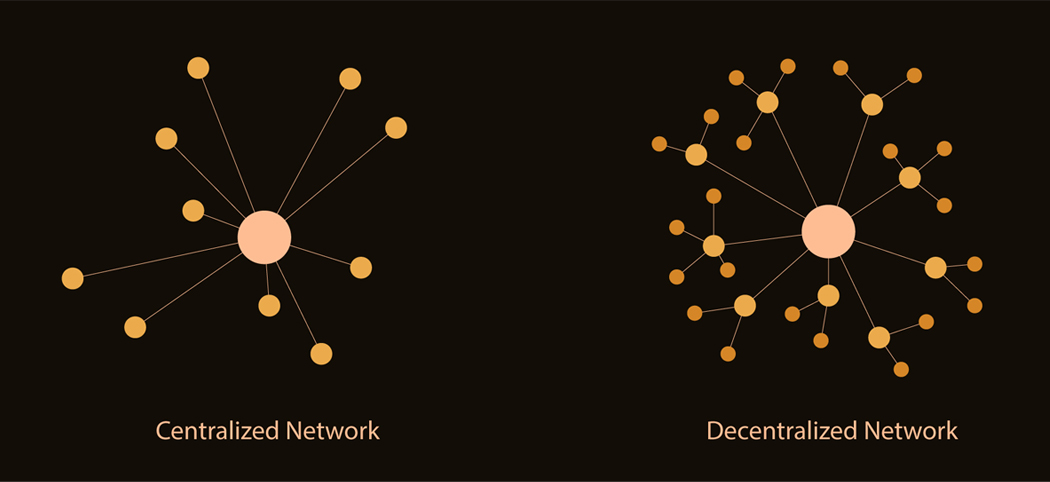
Decentralized
A public permissionless blockchain that no one fully controls

Market Potential
Blockchain will become the underlying infrastructure of the digital world in the future, and its economic value are vast..

Advantage of ecological development
Net Savings Link, Inc. (OTC: NSAV), a cryptocurrency, blockchain and digital asset technology company, whose vision is the establishment of a fully integrated technology company that provides turnkey technological solutions to the cryptocurrency, blockchain and digital asset industries.
Technology and Products
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) are a type of cryptocurrency exchange which allows for direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency transactions to take place online securely and without the need for an intermediary.

Yield Farming
When you deposit money in a bank, you’re effectively making a loan, for which you get interest in return. Yield farming, also known as yield or liquidity harvesting, involves lending cryptocurrency. In return, you get interest and sometimes fees, but they’re less significant than the practice of supplementing interest with handouts of units of a new cryptocurrency. The real payoff comes if that coin appreciates rapidly. It’s as if banks were luring new depositors with the gift of a tulip -- during the Dutch tulip craze. Or a toaster, if toasters were the object of wild speculation and price swings.
Liquidity Farming
Liquidity mining is the core of any defi projects, because those projects are typically not listed in any CEX and users must go to DEX liquidity pool to buy and sell. Therefore liquidity mining of new tokens must have a high APY to attract traders to provide liquidity, usually ranging from 1% daily to 6% daily. Without compounding, 1% daily equals to 365% profit over a year, ignoring the possibility that the LP token may decline in value (discussed separately below). With compounding, 1% daily would yield 101%^365-1 = 3,678%. At 6% compounded hourly or more frequently, we can see an APY exceeding hundreds of billions. Transaction fee is the major obstacle of compounding. Because Defi projects run on public blockchains, compounding requires the user to interact with the contract to put the earned interest into the LP token, and therefore triggers a transaction cost.

Decentralized Exchange vs. Centralized Exchange
Cryptocurrency exchanges provide a crucial source of liquidity to the global cryptocurrency market, facilitating billions of dollars in trading volume on a daily basis. As this market expands, leading exchange platforms continue to scale in response to the demand for digital assets, offering asset custody, new trading features and functionality, and access to an ever-growing number of digital assets. With disintermediation as a core philosophy of the blockchain community, decentralized exchanges — or DEXs — have gained in popularity alongside traditional centralized exchanges (CEXs).
Decentralized exchanges take a different approach to buying and selling digital assets: They operate without an intermediary organization for clearing transactions, relying instead on self-executing smart contracts to facilitate trading. This dynamic enables instantaneous trades, often at a lower cost than on centralized crypto exchanges. In the absence of intermediaries, DEXs take on a non-custodial framework. This means that you retain custody of your cryptocurrency and are responsible for managing your wallets and private keys. Holding your private keys is considered a boon to users who want to maintain complete control of their assets.
However, this comes with the risk that your keys could get lost, stolen, or destroyed; or in the unlikely possibility that you become incapacitated or pass away suddenly, if no one knows your password, your keys can’t be accessed. The lack of an intermediary also means that most DEXs have limited counterparty risk and are not required to follow Know-Your-Customer (KYC) or Anti-Money-Laundering (AML) regulatory standards.
The emerging DEX market encompasses distinct segments. Each platform uses various implementations of order books, liquidity pools, or other decentralized finance (DeFi) mechanisms like aggregation tools to offer novel and experimental financial instruments.
NSAV Exchange Advantages
Even in the earliest stages of development, decentralized crypto exchanges offer advantages that impact digital asset custody and diversity, transactional trust, trading fees, and investor privacy.

Custody: DEXs are non-custodial, which means traders don't need to relinquish the control of private keys to transact. Instead, externally held wallets interact with DEXs, and trades self-execute through smart contracts. Centralized exchanges, by contrast, play the role of custodian for your funds by controlling your private keys. This requires you to relinquish control of your private keys, but centralized exchanges offer trust and security.



Diversity: In October 2020, there were over 7,400 cryptocurrencies on the market. CEXs exercise control over the cryptocurrencies they will list, and will generally only list those with adequate trading activity, prevalence, and effective security standards to ensure profitability and legal compliance. Many altcoins are only accessible through DEXs, where P2P transactions can occur without high trading volumes. This provides a wider opportunity for engagement in digital assets and enhances financial inclusion.

Trustless Transactions: On CEXs, every transaction is overseen and recorded by a central authority, the exchange itself. Through smart contracts, DEXs execute trades and record them to the blockchain, enabling trustless transactions. And since DEXs do not hold your funds, they are less likely to be targeted by hackers.



Lower Fees: Decentralized exchanges function through the use of self-executing smart contracts. In the absence of an intermediary, DEXs use the same “gas” fee structure as the Ethereum blockchain they’re built on. DEXs charge a low fee, around 0.3% for exchanges like Uniswap. Although these fees fluctuate in response to the network utilization, they remain far lower than the costs incurred on centralized alternatives.

Privacy: Traders using decentralized exchanges don’t need to disclose their private keys because wallets are held externally, and the DEX is not liable for the funds. For the same reason, users aren’t typically required to complete KYC and AML procedures when using DEXs. While this may be advantageous in regards to convenience, it is potentially problematic from a legal perspective.

Deal Terms
-
Reg-S
Offering TypeThe type of investments that can be made into this asset. -
$100
Min. InvestmentThe smallest investment amount that this asset is accepting.


